Aging and Longevity : The Science Behind What Really Happens to Our Bodies Over Time
Aging is a natural, inevitable part of life, but how we age and the quality of those later years are not entirely beyond our control. Over time, our bodies undergo various changes that affect our physical health, cognitive function, and overall vitality. However, science has made significant strides in understanding the biological processes of aging and discovering ways to slow down or even reverse some of the effects.
In this article, we will explore the physiological changes that occur as we age, from the gradual decline in muscle mass and bone density to shifts in hormone production and cognitive function. We’ll also look at the latest scientific research on aging and longevity, focusing on what we can do to slow down the aging process and improve the quality of our lives as we grow older.
From nutrition and exercise to mental health and stress management, we will discuss actionable steps that can help promote longevity. The goal is to equip you with practical strategies to not only live longer but also to ensure that those extra years are healthy, vibrant, and fulfilling.
Understanding the science of aging is empowering—it allows us to make informed choices about how to age gracefully, while maximizing our potential for a long, active life. Let’s explore how to support our longevity with both a scientific approach and a mindful lifestyle.
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Aging and longevity involve complex biological processes, and the information provided is not intended to replace advice from a qualified healthcare provider. Always consult with a medical professional for personalized recommendations regarding aging and health.
Introduction
Aging is an inevitable journey that impacts every aspect of our bodies, from cellular structures to organ function. While no magic cure exists to stop aging, science has made significant strides in understanding how we age and how specific factors can enhance longevity.
This article delves into the complex biology of aging, explores the latest research, and offers practical tips to optimize health as we grow older.
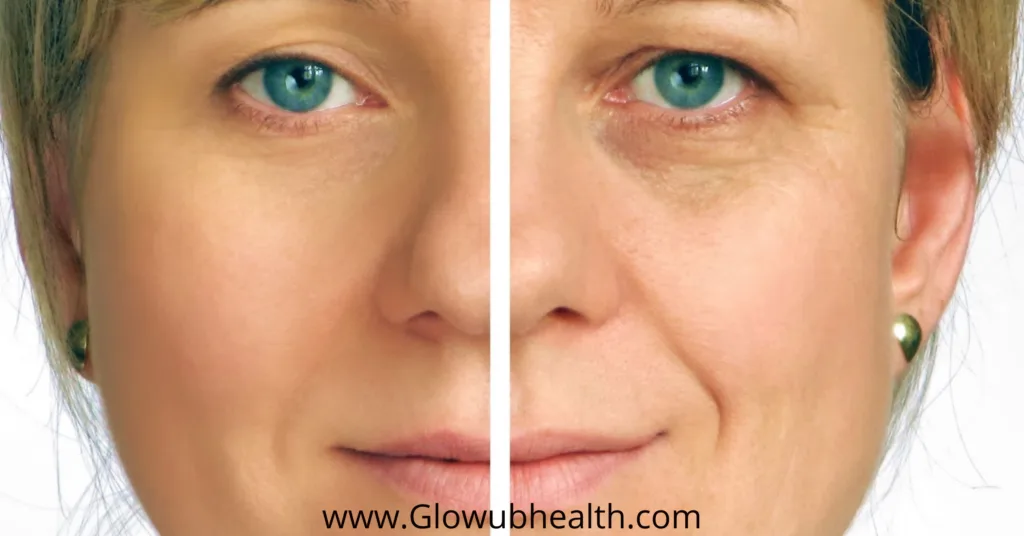
The Biology of Aging
Aging is not merely the accumulation of years but a dynamic process that affects our body at the cellular and molecular levels.
Scientific theories explain aging through a few key biological mechanisms:
- Cellular Senescence: As cells replicate, they gradually lose their ability to divide. This process, called senescence, prevents cells from replenishing and repairing tissues effectively, leading to physical signs of aging.
- DNA Damage and Repair: DNA undergoes damage daily due to environmental factors like UV radiation, toxins, and even cellular metabolism. Over time, DNA repair mechanisms become less efficient, which can lead to the accumulation of mutations associated with age-related diseases.
- Telomere Shortening: Telomeres are protective caps on the ends of chromosomes, which shorten each time a cell divides. Once telomeres reach a critical length, cells stop dividing, contributing to aging and reduced cellular function.
Understanding these mechanisms offers insights into interventions and lifestyle choices that can promote longevity and mitigate the effects of aging.
Key Factors that Influence Aging and Longevity

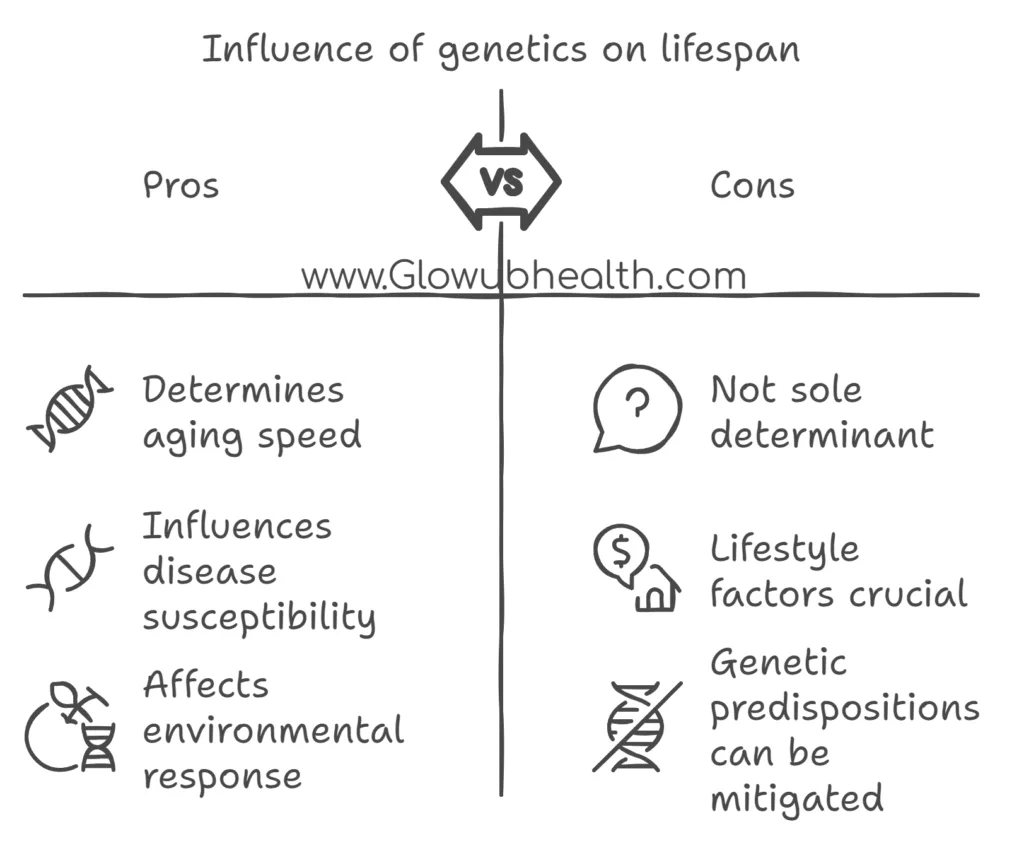
Genetics
Our genetic makeup plays a significant role in determining lifespan. Genes can influence how quickly we age, susceptibility to age-related diseases, and how we respond to environmental factors.
However, genes alone are not destiny; lifestyle factors often outweigh genetic predispositions when it comes to health and longevity.
Lifestyle Choices
Aging and longevity are heavily influenced by daily habits, including diet, exercise, and sleep patterns. Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor diet choices have been linked to accelerated aging, while a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and adequate sleep support long-term health.
Environmental Influences
Pollution, exposure to toxins, and socioeconomic factors also impact aging. Studies show that people in cleaner, less stressful environments with access to quality healthcare tend to live longer.
This reinforces the importance of a holistic approach to aging that considers both individual choices and external factors.
How Aging Affects Major Body Systems

As we age, different body systems experience functional declines, affecting overall health.
Here’s how aging impacts some of our primary systems:
Cardiovascular System
Aging commonly leads to stiffening of the blood vessels and increased blood pressure, placing more strain on the heart. This can lead to cardiovascular diseases, which are a leading cause of death among older adults.
Maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and monitoring blood pressure can support cardiovascular health as we age.
Musculoskeletal System
Loss of muscle mass, reduced bone density, and joint wear are typical effects of aging. This can lead to conditions like osteoporosis and arthritis, which impact mobility and quality of life.
Weight-bearing exercises and adequate calcium intake are crucial for musculoskeletal health.
Immune System
The immune system also weakens with age, a phenomenon known as “immunosenescence.” This makes older adults more susceptible to infections and slower to recover from illnesses.
A diet rich in antioxidants and regular vaccinations can help support immune health.
Read More: Best Immune Support Supplements for Adults: Top 10 That Work and Why
Nervous System
Age-related changes in the brain, such as reduced blood flow and neuron loss, can affect memory and cognitive function.
Engaging in mental activities, maintaining social connections, and managing stress can help preserve cognitive abilities.
Case Study: The Impact of Aging on Major Body Systems
John, a 68-year-old retired teacher, experiences age-related changes across multiple body systems. He notices fatigue and shortness of breath due to reduced cardiovascular efficiency, joint stiffness from declining bone density, and occasional memory lapses linked to mild cognitive decline.
His lung capacity has decreased, making physical activities more challenging, and he also reports digestive issues like constipation due to slower gut motility.
With guidance from his physician, John adopts lifestyle changes, including exercise, a high-fiber diet, and mental stimulation, to manage these changes and maintain his overall well-being.
Recent Advances in Aging and Longevity Research
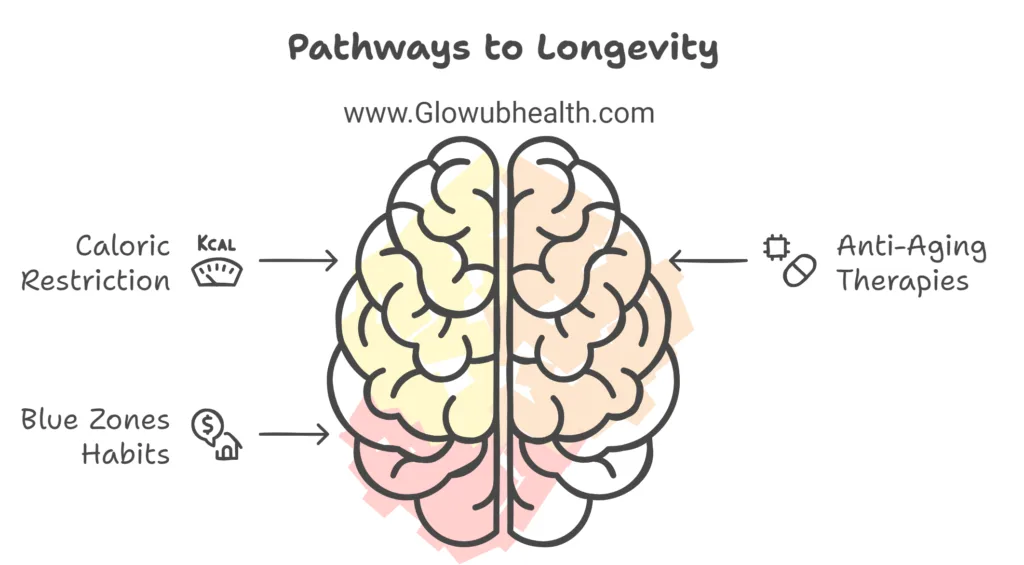
Caloric Restriction and Aging
Research on caloric restriction—reducing calorie intake without malnutrition—has shown promise in extending lifespan in animal studies.
Although the exact mechanism is not fully understood, caloric restriction appears to reduce cellular stress and slow the aging process.
Anti-Aging Therapies
Emerging therapies like senolytics (drugs that target senescent cells), stem cell treatments, and gene editing hold potential in combating the effects of aging.
While still in the early stages, these therapies could one day offer effective interventions for age-related diseases.
Blue Zones and Longevity Habits
“Blue Zones” are regions with high concentrations of centenarians, such as Okinawa, Japan, and Sardinia, Italy.
People in these areas typically follow plant-based diets, maintain active lifestyles, and prioritize social connections—lifestyle factors that contribute to longevity.
Actionable Tips for Healthy Aging and Longevity

To promote aging and longevity, here are practical steps supported by research and actionable insights:
Nutrition and Diet
- Adopt a Mediterranean or plant-based diet: Both diets are rich in antioxidants, fiber, and healthy fats, which protect cells and reduce inflammation.
- Incorporate anti-aging nutrients: Foods high in vitamins C and E, omega-3 fatty acids, and polyphenols, like berries, leafy greens, and nuts, support skin health and cellular function.
- Stay hydrated: Proper hydration is essential for skin elasticity and organ function, which are critical in slowing aging effects.
Read More: Balanced Nutrition: The Complete Guide to a Healthier Lifestyle
Physical Activity
- Prioritize strength training: Building muscle mass helps prevent age-related muscle loss and maintains metabolism.
- Engage in cardiovascular exercise: Activities like walking, cycling, and swimming improve heart health and endurance.
- Incorporate flexibility and balance exercises: Yoga and Pilates enhance mobility and reduce the risk of falls as we age.
Mental Health Practices

- Practice mindfulness and meditation: These activities reduce stress, which is linked to cellular aging.
- Stay socially connected: Strong relationships are linked to longer life expectancy, likely due to their positive impact on mental and emotional well-being.
- Challenge your brain: Puzzles, reading, learning new skills, and social interactions stimulate cognitive functions, helping prevent memory decline.
Read More: Maintaining Weight Loss : 12 Proven Strategies for Long-Term Success
Conclusion
Aging is indeed an inevitable journey, but it doesn’t have to be one marked by decline or diminished vitality. With the right mindset and daily habits, we can not only add years to our lives but enrich those years with purpose, energy, and fulfillment.
Understanding how lifestyle choices shape the aging process offers a sense of control over how we age. From the foods we eat to the relationships we nurture, these choices can either accelerate or slow down the aging process. Nutrition, exercise, mental health, and strong social connections form the foundation of healthy aging, allowing us to embrace life’s later stages with strength, clarity, and joy.
We now know that longevity is not just about the absence of disease but the presence of vitality and engagement in life. Research on centenarians in Blue Zones shows us that communities around the world live longer, healthier lives through simple, consistent habits like eating whole foods, staying physically active, and prioritizing strong social bonds. These habits are accessible to everyone, regardless of age, and can be integrated into our lives starting today.
Incorporating practices such as regular exercise, stress management, adequate sleep, and a nutrient-dense diet supports our body’s ability to function optimally as we age. But perhaps most importantly, cultivating a sense of purpose and joy enhances our mental well-being, keeping us active and engaged no matter what age we are.
Aging well is a holistic process, one that encompasses not just the physical aspects of health but also the mental, emotional, and social elements. It’s about nurturing the mind-body connection and making daily choices that enhance our overall well-being.
By embracing healthy aging principles, we can add life to our years and ensure that every decade is lived to its fullest potential.
FAQ
1. What is the science behind aging?
Aging involves biological processes like cellular senescence (when cells stop dividing), DNA damage, and telomere shortening. These factors cause physical changes, including skin wrinkles, muscle loss, and reduced organ function. Despite these changes, research suggests that lifestyle choices like diet, exercise, and stress management can slow down the aging process.
2. Can we reverse aging?
While there is no way to completely reverse aging, science is advancing with anti-aging therapies, such as stem cell treatments, senolytics (drugs targeting aging cells), and caloric restriction. These approaches may help delay the onset of age-related diseases but don’t yet offer a way to completely reverse aging.
3. How can I promote longevity?
Longevity can be supported by adopting a healthy lifestyle. This includes:
-A balanced, nutrient-rich diet, such as the Mediterranean or plant-based diet.
-Regular physical activity, including strength training and cardiovascular exercise.
-Mental health practices, like meditation and staying socially connected.
-Adequate sleep and stress management.
4. What are Blue Zones, and why are they important for longevity?
Blue Zones are regions of the world where people live significantly longer, often reaching 100 years or more. These areas include Okinawa (Japan), Sardinia (Italy), and Nicoya (Costa Rica). People in these regions follow lifestyles that emphasize plant-based diets, strong community ties, regular physical activity, and stress reduction, all contributing to their long lifespans.
5. Can genetics influence my lifespan?
Yes, genetics plays a role in aging and longevity. Some people may be genetically predisposed to live longer or have a higher risk of age-related diseases. However, lifestyle factors often have a stronger impact on your health and lifespan, making it possible to overcome genetic predispositions through healthy habits.
6. How does exercise affect aging?
Exercise is one of the most powerful tools for slowing down the aging process. Regular physical activity helps maintain muscle mass, bone density, cardiovascular health, and cognitive function. It also improves mood, reduces stress, and supports immune function, all of which contribute to longevity.
7. Does stress speed up aging?
Chronic stress accelerates the aging process by increasing inflammation and oxidative stress in the body, both of which damage cells and contribute to age-related diseases. Managing stress through mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and social support can help mitigate these effects.
8. What role does sleep play in aging and longevity?
Sleep is crucial for cellular repair, cognitive function, and overall health. Poor sleep is linked to a higher risk of chronic conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, and cognitive decline. Ensuring you get enough quality sleep supports both the aging process and longevity.
9. Are there supplements that can help with aging?
Certain supplements may support healthy aging, including:
–Omega-3 fatty acids: For heart health and inflammation reduction.
-Vitamin D: For bone health and immune support.
-Antioxidants: Such as vitamins C and E, which combat oxidative stress.
-CoQ10: For mitochondrial function and energy production.
However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplementation.
10. Can a plant-based diet increase longevity?
Yes, research suggests that plant-based diets, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts, can reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. These diets are high in antioxidants, fiber, and essential nutrients that support cellular health and longevity.
11. How can I maintain mental sharpness as I age?
Maintaining mental sharpness as you age can be achieved through continuous learning, brain exercises (like puzzles or reading), social interactions, and stress management techniques. Regular physical exercise also supports cognitive health by improving blood flow to the brain.






